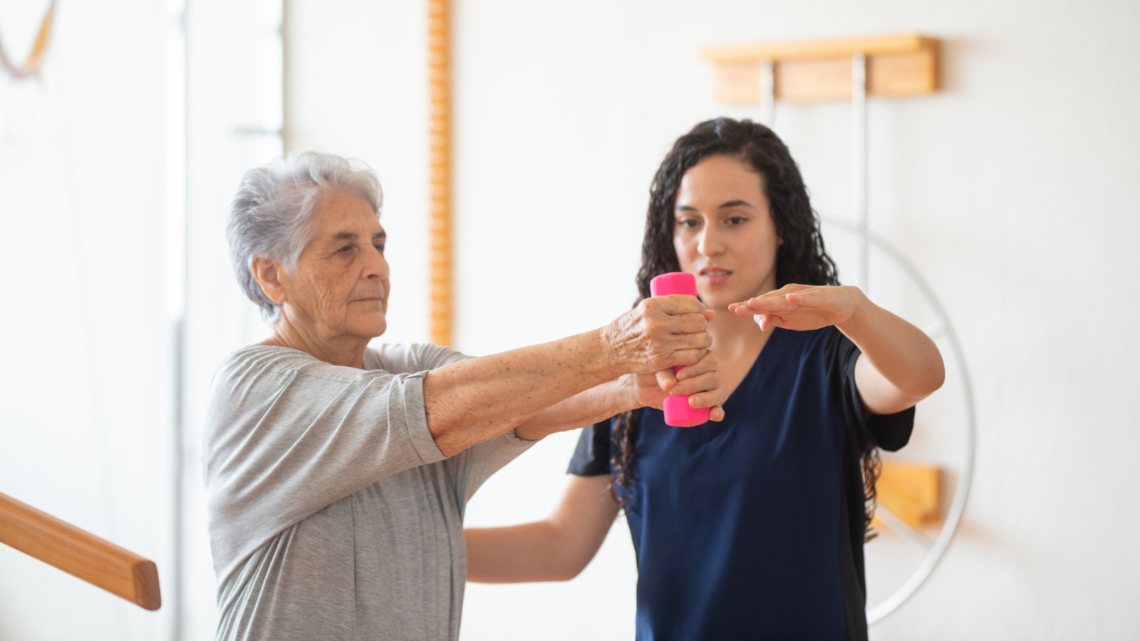
What is Occupational Therapy?
In today’s ever-evolving healthcare landscape, many Canadians may have come across the term “occupational therapy” without a clear understanding of what it entails.
What is Occupational Therapy?
Occupational therapy (OT) is a type of health care that helps individuals of all ages regain, develop, or maintain the skills they need to lead fulfilling lives. Contrary to what the name might suggest, it doesn’t focus solely on employment-related tasks but encompasses a broader range of daily activities.
Occupational therapists (OTs) are trained professionals who work with people to help them perform everyday activities, whether it’s tasks related to personal self-care, work, or leisure. Their goal is to help clients achieve independence, improve their quality of life, and participate more fully in their communities.
Why Might Someone Need Occupational Therapy?
There are several reasons one might be referred to or seek the expertise of an occupational therapist. Here are some common scenarios:
- Physical Rehabilitation: Following an injury, surgery, or medical condition like a stroke, OT can be invaluable. OTs help individuals regain lost skills, improve muscle strength, and adapt to their environment.
- Developmental Delays: Children with developmental challenges, like autism or cerebral palsy, might work with an OT to enhance their motor skills, sensory processing abilities, and everyday skills like dressing or feeding themselves.
- Mental Health: For those dealing with mental health challenges such as depression, anxiety, or PTSD, occupational therapy can provide coping strategies, stress management techniques, and structure to daily routines.
- Aging Population: As Canadians grow older, they may face challenges related to aging. OTs can help seniors maintain their independence by offering strategies to cope with memory loss, reduced mobility, or challenges related to daily living activities.
- Adapting to a New Environment: When someone has to move to a new living environment because of a disability or medical condition, an OT can recommend home modifications or adaptive devices, making it easier for them to live independently.
- Chronic Illnesses: Individuals with chronic illnesses, like arthritis or multiple sclerosis, might need OT to discover new ways of performing daily tasks with less pain or discomfort.
The Canadian Context
In Canada, occupational therapy services are offered in various settings, including hospitals, rehabilitation centres, schools, private practices, and clients’ homes. Provincial health plans, private insurance, and workers’ compensation boards often cover these services.
Occupational therapy is an integral part of a multidisciplinary approach to healthcare. It emphasizes the holistic well-being of the individual, ensuring that they can engage in meaningful activities irrespective of any physical, cognitive, or emotional challenges they might face.
If you or someone you know might benefit from occupational therapy, consider seeking a referral from your family physician or reaching out directly to an OT in your area. Remember, the ultimate goal is to enhance your quality of life and empower you to lead a fulfilling and independent life.