Neurological
-
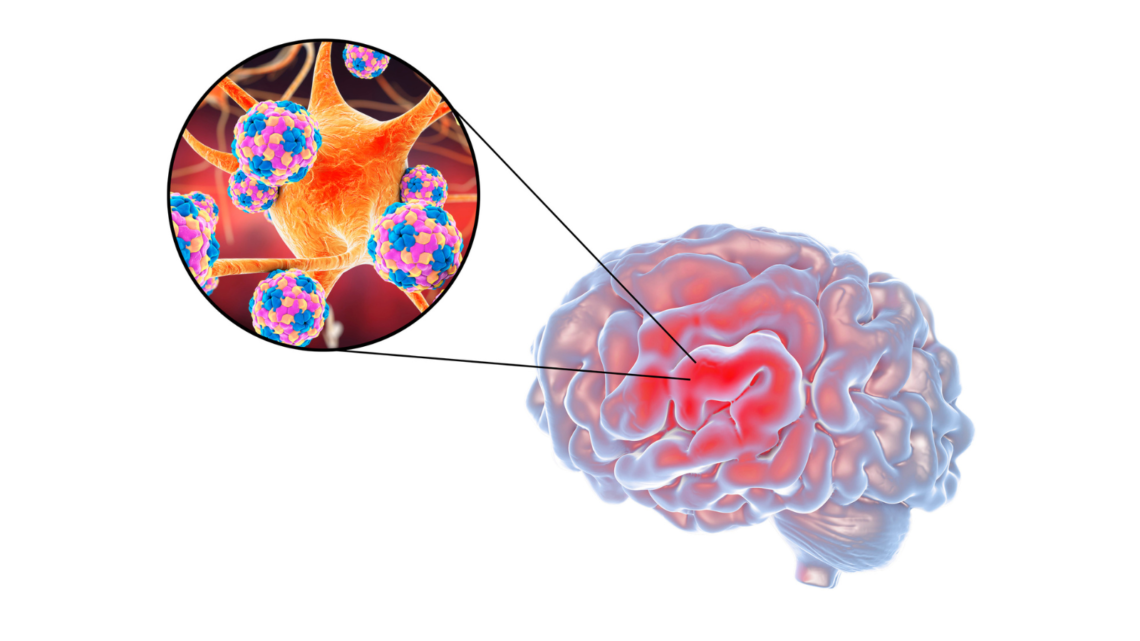
Meningitis Risks, Signs, and Prevention
Meningitis is a serious and often life-altering infection that has the potential to strike anyone, anywhere, and at any time, regardless of age or location. This illness, which affects the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, can lead to an array of severe symptoms and complications that highlight its devastating nature. Affecting over 2.5 million people worldwide each year, meningitis leaves a powerful impact on individuals and families alike, with fatal outcomes in approximately one out of every ten cases. The impact is especially heartbreaking in children under five, who account for nearly half of all meningitis-related deaths worldwide. Surviving meningitis often comes with its own challenges, as roughly…
-
Living with MS in Canada
Canada is recognized as having one of the highest rates of multiple sclerosis (MS) globally, with an estimated 90,000 Canadians currently living with this debilitating disease. The gravity of the situation becomes apparent when considering that, on average, 12 Canadians are diagnosed with MS every single day. This chronic illness predominantly affects individuals between the ages of 20 and 49, marking the beginning of a lifelong struggle against its unpredictable and often progressive nature. Multiple sclerosis is a complex neurological disorder that targets the central nervous system, encompassing the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. Classified as an episodic disability, MS is characterized by its varying severity and duration of…
-
Concussion Awareness
Concussions are a type of traumatic brain injury that result from a blow to the head or a sudden, violent motion that causes the brain to move within the skull. This movement can lead to temporary loss of normal brain function, affecting cognitive processes, physical abilities, and emotional well-being. Recognizing the signs of a concussion, knowing how to proceed with diagnosis and treatment, and understanding preventive measures are essential for managing this condition effectively. What Part of the Body Concussions Affect Concussions primarily affect the brain, the control center for all bodily functions. The brain is cushioned by cerebrospinal fluid within the skull, but a sudden impact or abrupt movement…
-
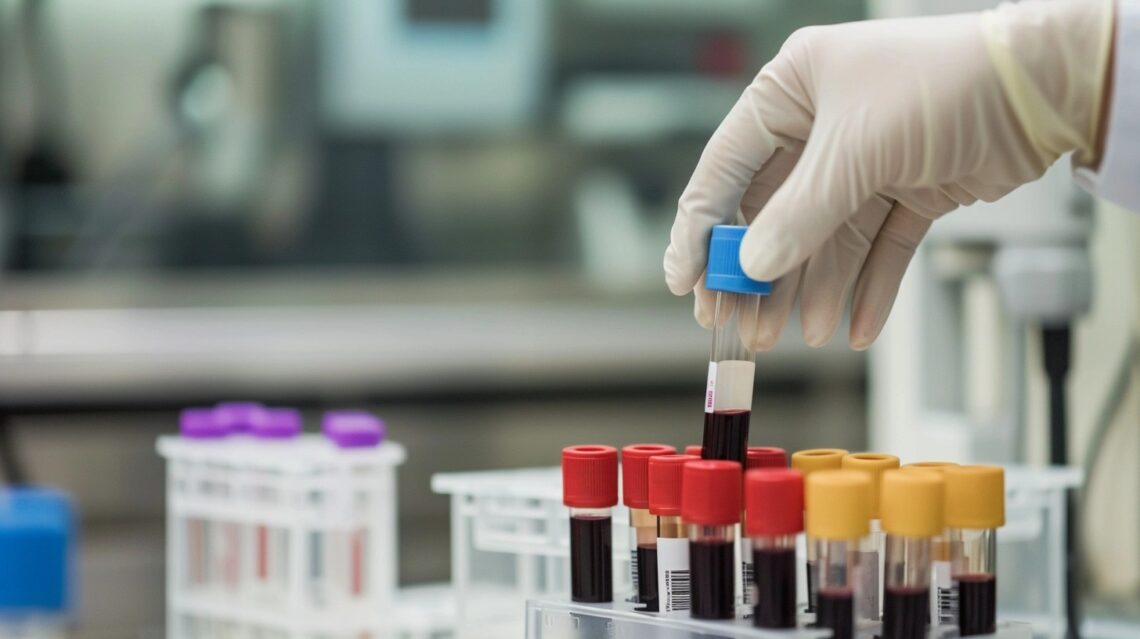
Breakthrough Blood Test for Alzheimer’s
In the continuously evolving and ever-expansive landscape of medical diagnostics, particularly in the domain of neurodegenerative diseases, a recent groundbreaking study has emerged, offering a beacon of hope for the early detection and, consequently, more effective management of Alzheimer’s disease. Central to this pivotal research is the innovative utilization of a blood test, specifically designed to detect the presence of a specific protein, known in the medical community as phosphorylated tau or p-tau. This development is not merely an incremental advancement; it represents a potential paradigm shift in our approach to diagnosing Alzheimer’s, promising not just early detection but also heralding a more accessible, cost-effective alternative to the traditional, more…
-
Managing Stress-Related Headaches
In the fast-paced rhythm of modern life, stress has become an inescapable companion for many, often manifesting itself through physical symptoms. One such common physical manifestation is stress-related headaches, a discomfort that a significant portion of the population experiences. Understanding the intricate link between stress and headaches, and learning how to manage these headaches, is essential for both physical and mental well-being. The Connection Between Stress and Headaches Headaches, in their various forms, are among the most prevalent health complaints. When we consider stress-related headaches, we primarily refer to tension-type headaches and migraines, both of which are significantly influenced by stress. Tension-type headaches, characterized by a dull, aching sensation and…
-
Understanding Alzheimer’s: A Guide for Canadians
January marks a significant month in Canada – Alzheimer’s Awareness Month. Spearheaded by the Alzheimer Society, this initiative sheds light on Alzheimer’s disease, a condition that touches the lives of many Canadians. Here, we delve into the intricacies of Alzheimer’s, exploring its nature, who it affects, and the impact it has on individuals, families, and society. What is Alzheimer’s Disease? Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that impairs memory and cognitive functions. It’s the most common form of dementia, accounting for 60-70% of cases. The disease is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain, leading to neuronal damage and brain atrophy. The Canadian…
-
PVNH Disorder
Periventricular Nodular Heterotopia (PVNH) is a rare neurological disorder that is characterized by the malpositioning of neurons in the brain. “Periventricular” refers to the region around the brain ventricles, and “nodular heterotopia” describes the presence of nodules, or small aggregations of nerve cells, that are out of place. During normal brain development, neurons migrate from their place of origin to their final destination. In PVNH, this migration is disrupted, and neurons form nodules in inappropriate areas, particularly near the ventricles. In most cases, PVNH is due to mutations in the FLNA gene, which encodes a protein crucial for cell movement and structure. This disorder follows an X-linked dominant inheritance pattern.…
-
Understanding the Types of Migraines
Migraines are far from a homogeneous affliction. The term “migraine” actually encompasses several different conditions, each with its own unique set of characteristics and symptomatology. The three primary types are migraine without aura, migraine with aura, and chronic migraine. Let’s delve into the intricacies of each. Migraine Without Aura Also known as a “common migraine,” migraine without aura is the most prevalent type of migraine. Despite its name, there’s nothing “common” about the intense pain and accompanying symptoms people experience. The pain is typically localized to one side of the head and can range from moderate to severe in intensity. It is often described as a throbbing or pulsating sensation.…
-
June is Migraine Awareness Month
June is Migraine Awareness Month, a critical period of focus on a medical condition that impacts an enormous number of individuals and households. This is especially true in Canada, where migraines are a prevalent issue. According to recent studies, migraines affect 25% of Canadian households. While this number may seem high, the reality of migraines is even more daunting. Within this 25%, between 1% and 2% of these individuals suffer from chronic migraines, a condition that involves having a headache for 15 or more days per month for at least three months. Chronic migraine is a severe neurological disorder that can disrupt lives, strain relationships, and affect a person’s ability…
-
What is Frontotemporal Dementia?
It was recently announced that Hollywood actor Bruce Willis had been diagnosed with frontotemporal dementia (FTD), an uncommon form of dementia. This has brought attention to a condition that is not as widely known as Alzheimer’s, the most common type of dementia. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of frontotemporal disorders, discuss their impact on those affected and their families, and explore the symptoms, diagnosis, and current treatment options. What is Frontotemporal Dementia? Frontotemporal dementia is a group of progressive neurological disorders that primarily affect the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. These areas are responsible for various cognitive functions, including decision-making, behavior, emotion, and language.…