Egg-cellent Benefits
Eggs, often hailed as a “superfood,” are a staple in many diets around the world. Beyond being versatile and delicious, eggs pack a significant nutritional punch, offering a range of health benefits. This article will delve into the nutritional profile of eggs, explore their health benefits, and discuss the healthiest ways to cook and consume them, with a focus on Canadian dietary guidelines and standards.
Nutritional Profile of Eggs
Eggs are a nutritional powerhouse, containing a variety of essential nutrients:
- Protein: A single large egg contains about 6 grams of high-quality protein, encompassing all nine essential amino acids.
- Vitamins: Eggs are a source of vitamins B2 (riboflavin), B12, D, A, and E, which play crucial roles in energy production, immune function, and eye health.
- Minerals: They provide important minerals like selenium, zinc, and iron, essential for antioxidant defense, immune function, and oxygen transportation in the blood.
- Choline: This lesser-known but essential nutrient supports brain health and is particularly important during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Particularly in eggs from hens fed omega-3 rich diets, these fats are vital for heart health and brain function.
Health Benefits of Eggs
- Supports Muscle Maintenance and Repair: The high-quality protein in eggs aids in muscle building, maintenance, and repair.
- Promotes Brain Health: Choline is essential for brain development and function, and eggs are one of the best dietary sources.
- Enhances Eye Health: Lutein and zeaxanthin, antioxidants found in egg yolks, contribute to eye health and may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
- Supports Heart Health: While eggs do contain cholesterol, recent studies indicate that for most people, the dietary cholesterol in eggs has a minimal effect on blood cholesterol levels. The presence of omega-3 fatty acids also supports heart health.
- Weight Management: The protein content in eggs can increase feelings of fullness and reduce calorie intake at subsequent meals, aiding in weight management.
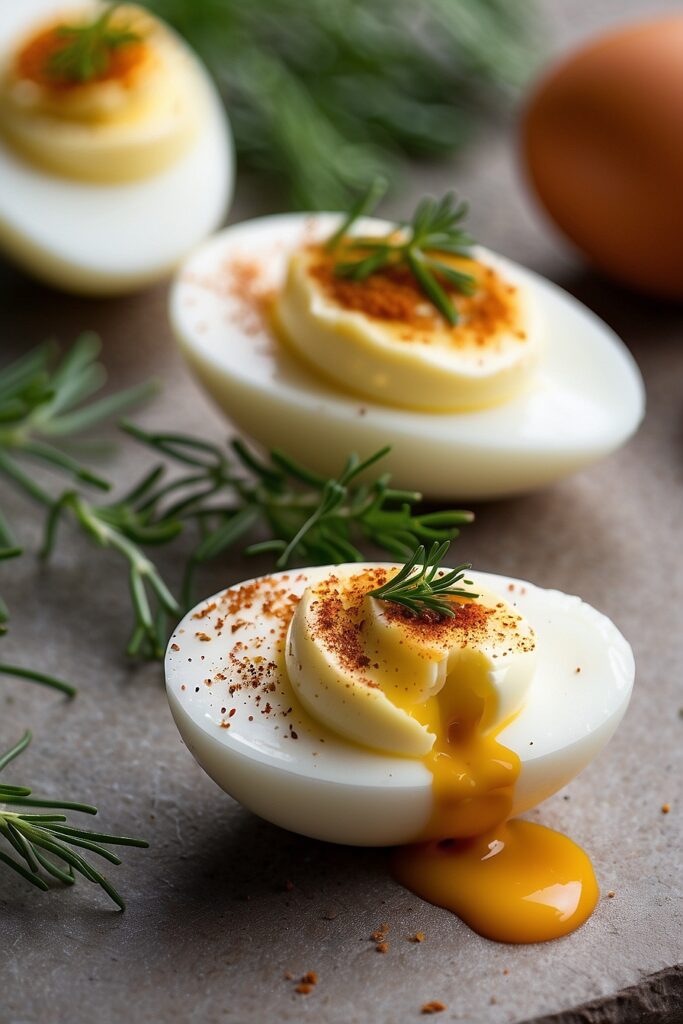 Ways to Cook and Eat Eggs
Ways to Cook and Eat Eggs
While eggs are inherently nutritious, the way they are prepared can significantly impact their health benefits:
- Boiled Eggs: Hard-boiled or soft-boiled eggs are among the healthiest options. They don’t require added oil or butter, preserving their natural nutrient profile.
- Poached Eggs: Poaching eggs is another healthy method, as it also does not require added fats. Ensure the water is not too hot to avoid overcooking the yolks, which can reduce the levels of heat-sensitive nutrients.
- Scrambled Eggs or Omelettes: These are healthy options when minimal butter or oil is used. Incorporating vegetables can enhance their nutritional value.
- Baked Eggs: Eggs baked in avocados or in a tomato sauce (shakshuka) are nutritious options that add extra vitamins and antioxidants.
- Fried Eggs: If frying eggs, it’s advisable to use a small amount of olive oil or a non-stick pan to reduce the need for extra fat.
- Devilled Eggs: When preparing devilled eggs, start by hard boiling the eggs to ensure the yolks are firm and easy to remove. After cooling and peeling, carefully halve the eggs and scoop out the yolks. Mix the yolks with ingredients like mayonnaise, mustard, and seasonings to create a smooth, flavorful filling. This mixture is then piped back into the egg whites, creating the classic deviled egg appearance. For an extra touch, garnish with paprika or fresh herbs before serving. This method ensures a delightful blend of creamy texture and savory taste in every bite.
Considerations and Recommendations
- Portion Control: While eggs are healthy, moderation is key. Canadian dietary guidelines recommend including a variety of protein sources in your diet.
- Quality of Eggs: Opt for organic or omega-3 enriched eggs when possible, as they have a higher nutritional content.
- Dietary Restrictions: Those with specific health conditions, like high cholesterol, should consult with a healthcare provider about egg consumption.
- Food Safety: Properly store and cook eggs to reduce the risk of salmonella and other food-borne illnesses.
Eggs are a nutrient-rich food that can play a vital role in a balanced diet. They offer high-quality protein, essential vitamins and minerals, and beneficial fats. When prepared healthily, they contribute to muscle health, brain function, eye health, and heart health, supporting overall well-being. Incorporating eggs into your diet, considering the healthiest cooking methods, and adhering to dietary guidelines can help maximize their health benefits while enjoying their versatility and taste.
References
- Health Canada. (2021). Canada’s Food Guide.
- Fernandez, M. L. (2010). Effects of eggs on plasma lipoproteins in healthy populations. Food & Function.
- Zeisel, S. H., & da Costa, K. A. (2009). Choline: An essential nutrient for public health. Nutrition Reviews.